GLUCOSE POST PRANDIAL
Original price was: ₹50.00.₹40.00Current price is: ₹40.00.
Postprandial blood sugar — the level of sugar in your blood after you eat and drink — is an important indicator of metabolic and overall health. Monitoring your postprandial blood sugar levels can help you to understand your personal responses to the foods you eat. It’s normal for your blood sugar to rise after you eat and then fall again as the cells in your body take in the sugar from your blood to use for energy or to store for later. But blood sugar that’s consistently too high isn’t
Well Established ISO 9001 Certified Centres
- Precision Reports
- Sri Divya uses Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) 128-bit encryption
- Transparent Reports
- Advanced Pathology
Description
GLUCOSE POST PRANDIAL
What is Post-Prandial Blood Sugar?
In medical terminology, post-prandial means after eating a meal. Therefore, post-prandial blood sugar refers to the blood glucose levels after eating a meal. You might be wondering why is it important to measure your post-prandial blood sugar levels?
The answer is that the post-prandial blood sugar levels allow you to examine the insulin activity in your body. Your blood sugar levels surge high every time you eat your meals. However, this happens because the glucose from the food particles gets rapidly absorbed into the blood flow.
The increase in this blood glucose level triggers insulin hormone to show up. Insulin then starts metabolising glucose molecules into energy molecules. Therefore, this is the reason why you should be interested in your post-prandial blood glucose levels. However, this basic mechanism gets altered in people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
For example, suppose you are hypoglycemic (type 1 diabetic). In that case, your body is producing insulin in insufficient amounts, which leads to an upsurge in the blood glucose levels as counter hormone insulin is absent.
Similarly, if you are hyperglycemic (type 2 diabetic), your body has an inherent resistance toward insulin, making the glucose metabolism process slower. Again, this results in spiked blood sugar levels, which may be a cause of concern.
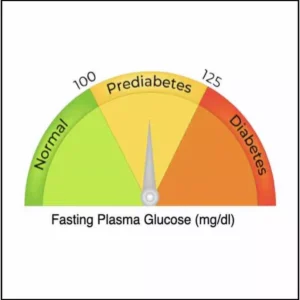
What are normal and high levels of postprandial blood sugar?
Typically, blood sugar levels peak between 1 and 2 hours after eating, when the carbohydrates in your food have been broken down into glucose — or sugar — and this has entered your bloodstream.
To test your postprandial blood sugar responses, healthcare professionals can use an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT).
For this test, a healthcare professional measures your blood glucose before and 2 hours after you drink a special sweet drink that contains 75 grams of glucose. The results indicate the following:
A postprandial blood sugar measurement below 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) is considered normal.
If your levels are between 140 and 199 mg/dL (7.8 and 11 mmol/L), it indicates that you may have prediabetes.
A reading of 200 mg/dL ( 11.1 mmol/L) or higher suggests that you have diabetes, but your doctor may use more than one test to make a diagnosis.
These values are specific for the OGTT test and the high amounts of sugar in the drink that you consume as part of it.
For adults who are living with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommend specific postprandial blood glucose target ranges to aim for during everyday life:
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes: Less than 180 mg/dL (10 mmol/L)
Gestational diabetes: Less than 120 mg/dL (6.7 mmol/L)
For people without diabetes, there aren’t any guidelines for postprandial blood sugar levels when eating their normal diet.
The thresholds that healthcare professionals use for making a diabetes diagnosis are specific to the OGTT test.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.